reportable range vs linearity|reportable range chart : distribute Reportable range refers to the span of results within which the method performs acceptably in terms of sensitivity, linearity and reproducibility WEBfatalmodel-com.garotadeprograma.net. Verifying you are human. This may take a few seconds.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Descubra todas as ofertas de streaming para ver o filme Harry Potter e a Pedra Filosofal. Assistir ao filme "Harry Potter e a Pedra Filosofal" em VOD com AdoroCinema
It is crucial to know the upper and lower limits of a test's reportable range. Elsa gives a step-by-step explanation of how to prepare and calculate the experiment that determines the range, using a cholesterol example as well as two Javascript worksheet calculators.This zoom will cover the factors to consider in designing and conducting a reportable range study, the benefits of commercial linearity kits vs. manual dilutions, and the data collection, analysis, . Reportable range refers to the span of results within which the method performs acceptably in terms of sensitivity, linearity and reproducibility The table of performance characteristics vs validation tests has been updated: Linearity has been replaced by “Working Range” and consists of “Suitability of calibration model” and “Lower Range Limit verification” (QL/DL).
Reportable range (CLIA §493.2) 3 means “the span of test result values over which the laboratory can establish or verify the accuracy of the instrument or test system measurement response.” (In CAP's definitions, the .
It’s often called reportable range, but measuring interval, analytical measurement range, and linear range each refer to the same characteristic. Verifying a test’s reportable range relies on selecting samples . For quantitative tests, the manufacturer’s limits of detection, linearity, reportable range and precision must all be validated or verified by the lab. Table 1 shows the updated .
analyzing a laboratory investigation answers
A clinically reportable range (CRR) is another proposed concept of the CLIA reportable range by CAP. It is similar to AMR but assumed to refer the wide range of analyte results, including .
§ Linearity: As defined by the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) EP06-A Guideline, linearity is the ability, within a given range, to provide results that are directly proportional to the concentration of the .Example Reportable Range Experiments (Linearity) Example Analytical Sensitivity Experiments Example Precision Experiments Example Accuracy Experiments Example Reference Range Determination Example Laboratory Test Method List Example Quality Management Planreportable range. For modified FDA-cleared or approved tests and laboratory-developed tests (LDTs), the laboratory must establish accuracy, precision, analytical sensitivity, interferences, analytical specificity, and reportable range, as applicable; data on interferences may be obtained from manufacturers or published literature, as applicable.
The reportable range is defined by CLIA as »the span of test result values over which the laboratory can establish or verify the accuracy of the instrument or test system measurement response.« However, CAP defines the reportable range in the context of two distinct concepts; the analytical measurement range (AMR) and the reportable clinical .
Reportable range identified through linearity experiments. This characteristic is the span of test results for which you can verify accuracy. It’s often called reportable range, but measuring interval, analytical measurement range, and linear range each refer to .Validating the reportable range, historically called “linearity”, is one of the very first studies a laboratory needs to perform with a new method or instrument. It’s also one of the studies that must be repeated throughout the instrument’s lifetime, often at 6 month intervals. The objective of a reportable range study is to assess the• The laboratory has determined that the test system’s reportable range for patient test results should be checked more frequently. Reminder: The laboratory is responsible for verifying calibration on factory-calibrated test systems that cannot be calibrated by the user. What materials should I use to perform calibration verification?Analyzer. The reportable range of the i-STAT ACT test is from 50-1000 seconds. The i-STAT ACT tests have demonstrated linearity between 0.0 and 6.0 units of heparin in blood samples from normal, healthy volunteers. An in vitro heparin sensitivity curve was generated by adding increasing amounts of heparin to aliquots
Verifying a test system’s accuracy, precision and reportable range may be performed using the same samples. For example, you may test samples with known values at the upper and lower end of the manufacturer’s reportable range, along with samples that are in the normal range for your patient population, in different runs To additionally complicate things, the College of American Pathologists (CAP) further delineates reportable range as being the analytical measuring range (AMR), meaning “the range of numeric results a method can produce via the normal measuring process and without any special specimen pretreatment, such as a dilution.”
Linearity and Calibration Verification Assesses accuracy, reportable range, and linearity by analyzing more than 3 specimens with predefined concentrations. Simple Accuracy Assesses accuracy by testing whether replicate measurements lie within a predefined target range. EP6 Linearity Verifies linearity using the CLSI EP6 protocol that offersThe Quality System for LGC Clinical Diagnostics, Inc. is registered to ISO 13485:2016 by DEKRA Certification B.V. ® 2001- 2024 VALIDATE is a registered trademark of .2) Linearity of the XN-550 The linearity of a hematology instrument can be verified by comparing the laboratory's reportable range with commercially available linearity assays. RANGE CHECK™ III and RET-CHECK™ II for reticulocytes were used to verify the linearity of the XN-550 throughout its full range.The expedited linearity evaluation provides the opportunity to verify your submitted results, review your linearity evaluation, and submit any necessary data corrections prior to the start of the CVL Survey processing. If data revisions are submitted prior to the survey due date, we will generate another expedited linearity evaluation.
throughout the reportable range for patient test results. Which laboratories are required to perform calibration and calibration verification? In general, laboratories using non-waived test systems are required to perform calibration and calibration verification. It is not a requirement for waived test systems, unlessReportable Range. •Method Verification •Whenever a new test is introduced/ new instrument put in place. •MV is done before the new test/ instrument is used on patients. •It includes verifying the reportable range by doing a linearity study. •Linearity study: •Checks that the reportable range gives you an accurate result by runningReportable range (CLIA §493.2)3 means ‘‘the span of test result values over which the laboratory can establish or verify the accuracy of the instrument or test system measurement response.’’ (In CAP’s definitions, the reportable range .
analyzing a laboratory investigation chapter 5
determined range of analyte values. Linearity testing is only required for measured analytes, and not required for calculated analytes. Consult the instrument user’s manual to determine . •A minimum of 5 samples that cover the reportable range of the method. •When plotted, the values should ideally be equidistant from each other.
the lower and higher reportable range. More samples must be included to validate the performance of the instruments at the lower and upper limits of the reportable range. Table 1: HbA1C data for the test method (Y) and the comparison method (X) (N=40) Table 2: Summary of the data statistics and a brief description of the hemoglobin A1C
Learn more about Calibration Verification and Linearity (CVL). Watch our two-part educational video series to facilitate implementation in your laboratory. Part One. Understanding the Requirements of Analytical Measurement Range (AMR) Verification . Learn basic terminology; Identify checklist requirements and appropriate material for verification The linearity of a sample is related to many factors, including the chemical composition of the sample and the path length the light must travel. An unknown sample should always be tested for linearity. Dynamic Range. Dynamic range refers to the range of concentrations an instrument can read, from the minimum to the maximum detectable.– Range of analyte where results are proportional to the true concentration of analyte in the sample – Range over which the test can be performed w/o modification (e.g. no dilution) • Also called: Dynamic Range, and Reportable range • Determined in the lab by linearity experiments
analyzing a laboratory investigation chpt 5
For quantitative tests, the manufacturer’s limits of detection, linearity, reportable range and precision must all be validated or verified by the lab. Table 1 shows the updated requirements for quantitative tests. Table 1. Summary of Performance Characteristics Required Depending on Qualitative Test Type1 The loss of linearity response has lost its linearity at both the upper and lower ends of the data range. Figure 3. Linear plot of data without bias (circles). Linear plot of data showing proportional bias as indicated by a slope of 1.2 (triangles). Linear plot of data showing constant bias as indicated by a y-intercept of 1.8 (squares) Reportable range identified through linearity experiments. This characteristic is the span of test results for which you can verify accuracy. It’s often called reportable range, but measuring interval, analytical measurement range, and linear range each refer to .
Reportable range includes all the values from the lowest to the highest results that can be accurately measured by the assay. Calibration verification verifies the assay’s calibration throughout this entire claimed range ensuring accurate patient results. . Calibration Verification with Linearity Experiements - When Should Non-Linearity .
A range of performance characteristics may be required to be verified or validated (see the Glossary (page 33) for definitions): • Accuracy • Precision (reproducibility) • Analytical sensitivity • Analytical specificity • Reportable range/intervals (normal values) • Reference range
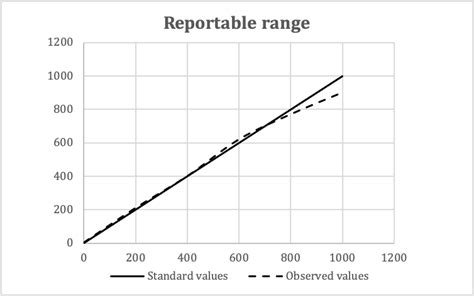
validation of reportable range
web8 de dez. de 2021 · Neste video eu mostro em detalhes como você ENVIA DINHEIRO PARA A CORRETORA VIA NETELLER USANDO O PIX. É bem simples e aqui tem o passo a passo. Para você qu.
reportable range vs linearity|reportable range chart